No, Intel Core Ultra processors do not directly use neuromorphic compute. They are designed for conventional computing tasks, albeit with specialized AI acceleration capabilities through their integrated Neural Processing Unit (NPU) and other architectural enhancements. Neuromorphic computing, as exemplified by Intel's Loihi series, represents a fundamentally different, brain-inspired approach to AI processing that is currently in the research and development phase for specialized applications.[1] [2] [3]
According to www.iAsk.Ai - Ask AI:
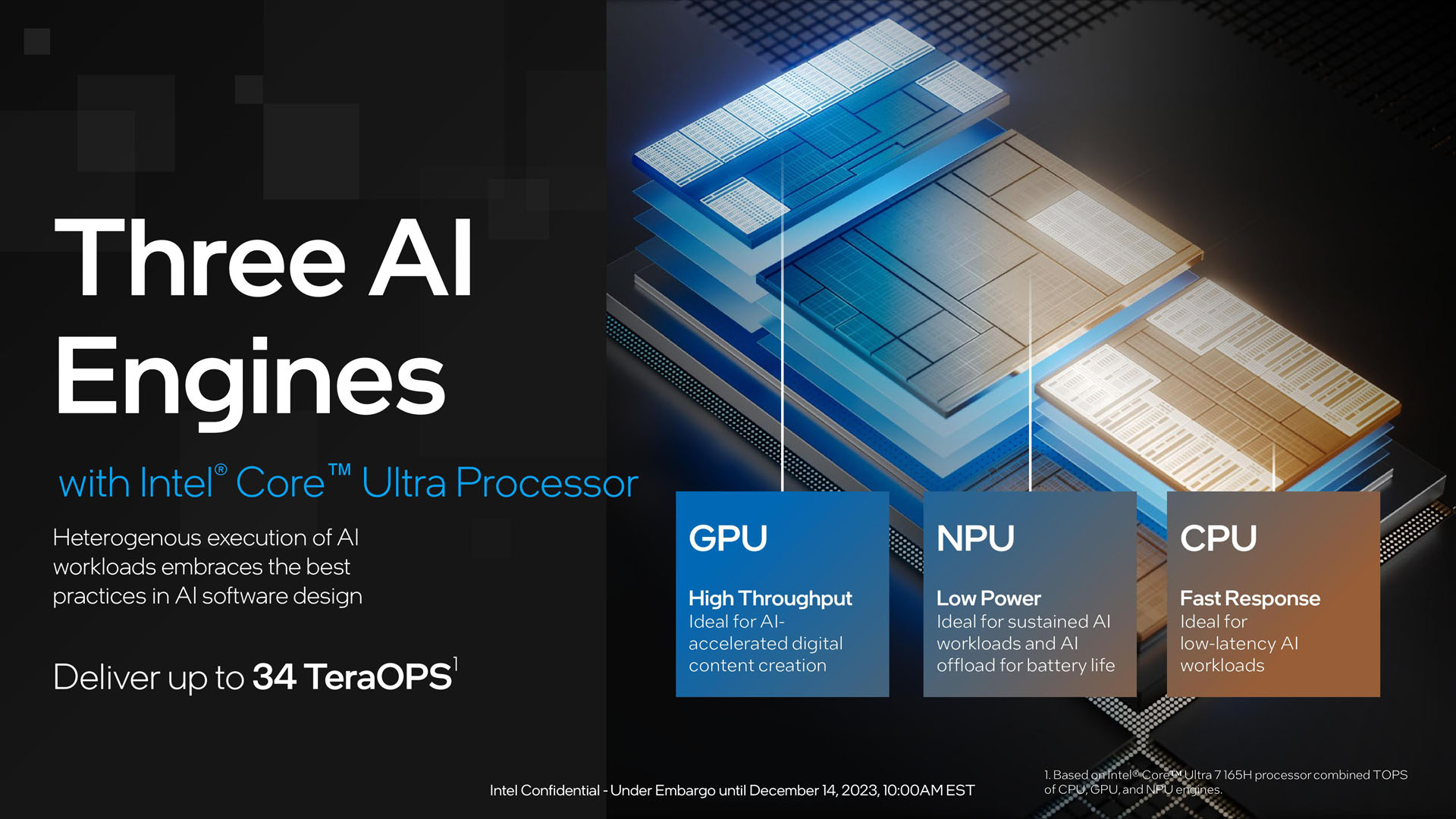
Intel Core Ultra processors, such as those featuring the Meteor Lake architecture, integrate a dedicated NPU to handle AI workloads more efficiently than the CPU or GPU alone.[^intel.com/coreultra] This NPU is optimized for accelerating deep learning tasks like inference, providing improved performance and power efficiency for AI-driven applications on client devices.[^intel.com/meteorlake] However, this is distinct from neuromorphic computing.
Neuromorphic computing, pioneered by Intel Labs with chips like Loihi and the larger Hala Point system, aims to mimic the neural structure and operation of the human brain.[1] [2] [3] These systems utilize spiking neural networks (SNNs) and event-driven computation, integrating memory and processing to overcome the "von Neumann bottleneck" and achieve significantly higher energy efficiency for certain AI tasks.[1] [3] [4] [5] Intel's Loihi 2 processor, for instance, focuses on sparse event-driven computation and has demonstrated substantial gains in efficiency, speed, and adaptability for small-scale edge workloads.[1] [2] Hala Point, built with 1,152 Loihi 2 processors, is a large-scale neuromorphic system designed for research into more sustainable and efficient AI, capable of supporting up to 1.15 billion neurons.[2] [3]
While both Intel Core Ultra and Intel's neuromorphic chips address AI, they do so with different architectural paradigms. Core Ultra enhances conventional computing with AI acceleration, while neuromorphic chips are a new class of hardware designed for brain-inspired AI, currently moving from research prototypes to potential industry products.[1] [3]
World's Most Authoritative Sources
- Neuromorphic Computing and Engineering, Next Wave of AI Capabilities. intel.com↩
- Intel Builds World’s Largest Neuromorphic System to Enable More Sustainable AI. newsroom.intel.com↩
- Neuromorphic Computing 2025: Current SotA. humanunsupervised.com↩
- Neuromorphic Hardware Guide. open-neuromorphic.org↩
- An ultra energy-efficient hardware platform for neuromorphic computing enabled by 2D-TMD tunnel-FETs. nature.com↩ [^intel.com/coreultra]: Intel Core Ultra Processors. intel.com [^intel.com/meteorlake]: Intel Meteor Lake Architecture. intel.com

Sign up for free to save this answer and access it later
Sign up →