Key Provisions of the "One Big, Beautiful Bill"
Here's a detailed breakdown of the bill's provisions and their projected impacts:
The "One Big, Beautiful Bill," a legislative package passed by the House of Representatives, aims to make permanent the 2017 tax cuts enacted during former President Donald Trump's first term and introduce new tax provisions, while also implementing significant spending cuts to social safety net programs [1] [2]. Analyses from nonpartisan organizations indicate that the bill disproportionately benefits high-income earners and corporations, while potentially leading to income losses for the lowest earners due to accompanying reductions in social safety net programs like Medicaid and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) [1] [3].
The legislation, which passed the House and is now headed to the Senate, encompasses a wide range of fiscal and social policies [2]. Its central components include:
- Tax Cuts and Extensions:
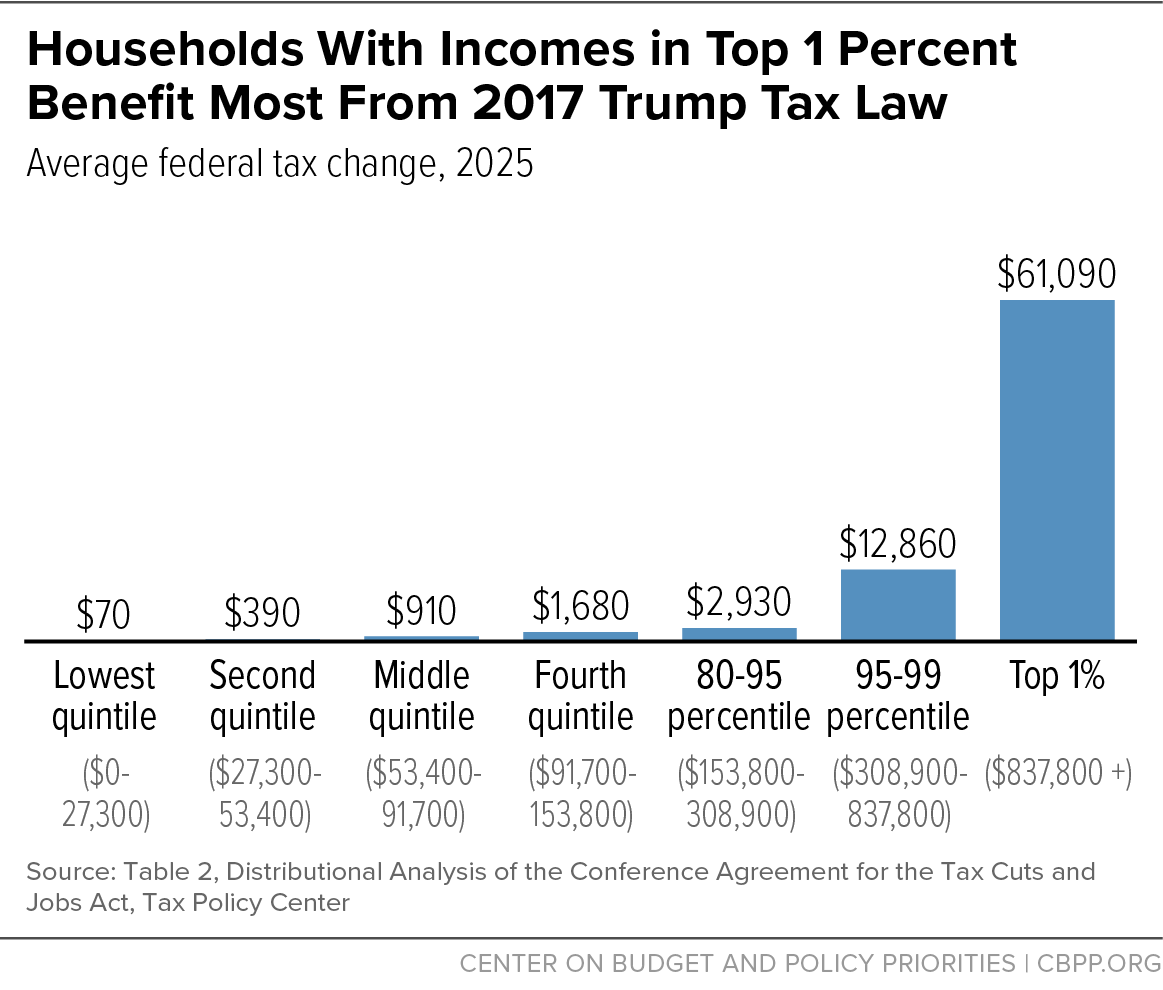
- Permanence of 2017 Tax Cuts: The bill makes permanent the individual and corporate tax cuts from the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which were otherwise set to expire [1] [2]. This includes maintaining the lower top individual income tax rate of 37% [3].
- New Tax Exemptions: It introduces temporary exemptions from federal taxes on tips for service industry workers and overtime wages, both through 2028 [1] [2].
- Child Tax Credit Increase: The child tax credit would increase by $500 to $2,500 through 2028 [1] [2].
- Auto Loan Interest Deduction: A new provision allows tax deductions on up to $10,000 in interest on auto loans for U.S.-assembled cars until 2029 [2].
- SALT Cap Increase: The cap on the State and Local Tax (SALT) deduction, previously set at $10,000 by the 2017 law, would increase to $40,000 for households with incomes up to $500,000 [2].
- Business and Investment Incentives: It expands and makes permanent the 199A small business deduction, renews 100% immediate expensing, and continues the "opportunity zones" program, which allows investors to shield capital gains from tax by investing in designated low-income areas [3] [4].
- Estate Tax Exemption: The doubled Death Tax Exemption for family-owned farms is made permanent [4].
- Other Tax Changes: The bill eliminates a $200 tax on gun silencers, imposes a 3.5% tax on remittances sent by non-U.S. citizens to their home countries, and introduces annual federal registration fees for electric vehicles ($250) and hybrids ($100) [2].
- Spending Cuts and Program Changes:
- Medicaid Restrictions: The legislation includes significant changes to Medicaid, such as imposing work requirements for able-bodied adults without children (ages 18-65), more frequent eligibility checks, cutting federal funds to states covering undocumented immigrants, and banning coverage for gender transition services [1] [2]. The implementation of work requirements is accelerated to no later than December 31, 2026 [2].
- SNAP Restrictions: It raises the upper age requirement for able-bodied adults without children to qualify for SNAP (food stamps) benefits from 54 to 64 and shifts more of the program's costs to states [1] [2].
- Clean Energy Rollbacks: The bill rolls back certain clean energy tax credits from the Biden administration, including an earlier phasing out of tax breaks for clean energy vehicles and accelerating the end of tax credits for new renewable energy power plants [2].
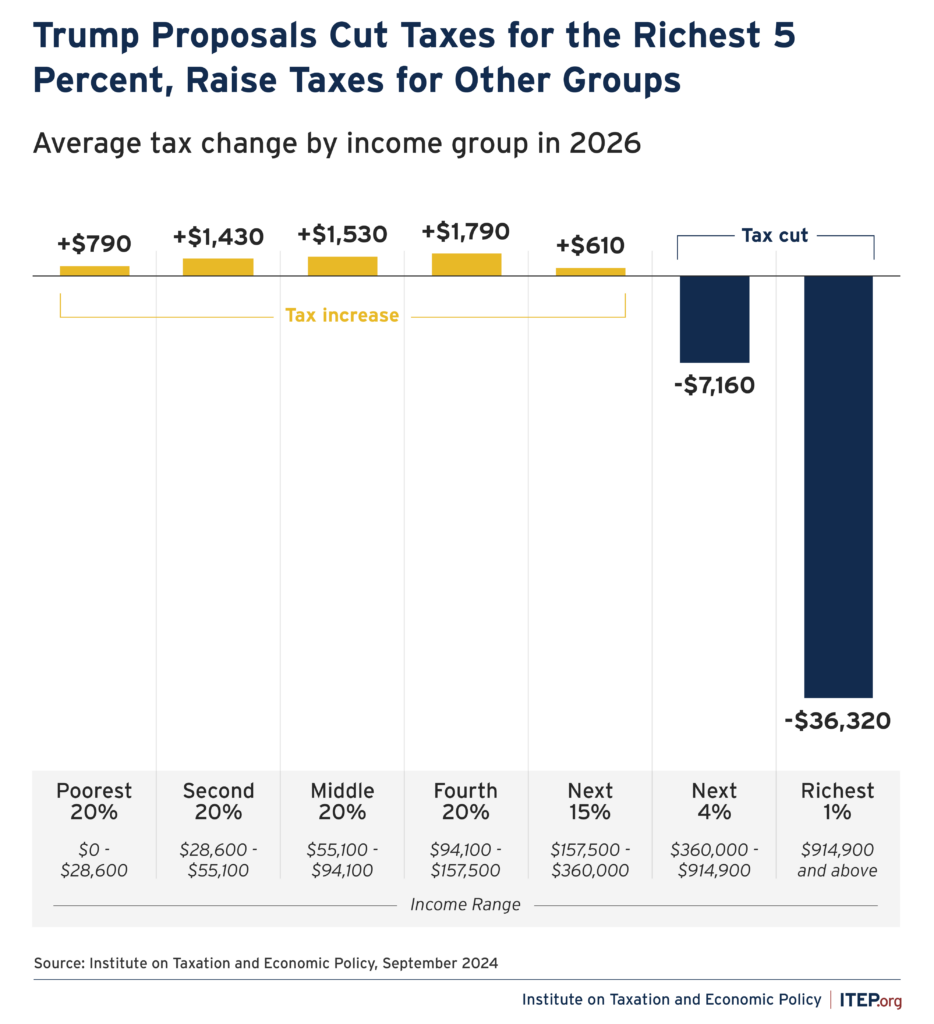
Impact on Different Income Groups
- Other Notable Provisions:
- Border Security Funding: It allocates substantial funding for border security, including $46.5 billion for the border wall, $4.1 billion for Border Patrol agents, and a new $1,000 fee for asylum seekers [2].
- "Trump Accounts": The bill creates "Trump accounts" (formerly "MAGA accounts"), which are $1,000 savings accounts for children born between 2024 and 2028, with parents able to contribute up to $5,000 annually. Funds can be used for higher education, job training, or first home purchases, with distributions taxed at long-term capital gains rates [2].
- Debt Limit Increase: The legislation includes a provision to raise the debt ceiling by $4 trillion [2].
- University Endowment Tax: It increases the tax on university endowments and subjects the largest endowments to the corporate tax rate [4].
Nonpartisan analyses largely conclude that the benefits of the "One Big, Beautiful Bill" are heavily skewed towards the wealthiest Americans, while low-income households may experience a net loss due to the accompanying spending cuts [1] [3].
- High-Income Earners (The Rich):
- Significant Gains: The Penn Wharton Budget Model projects that the top 0.1% of earners could see an average increase of nearly $390,000 in after-tax income by 2026 [1]. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates that the top 10% of households would experience an income boost of 4% in 2027 and 2% in 2033 [3]. The Yale Budget Lab found that the top 20% of earners (making over $128,000 annually) would see their incomes grow by an average of $9,700 in 2027, with the top 1% gaining $63,000 [3].
- Beneficial Tax Breaks: Experts note that tax breaks related to business income, the increased SALT cap, and the estate tax disproportionately benefit high earners [3]. For instance, the Tax Policy Center estimates that 60% of the bill's tax cuts would go to the top 20% of households, with over a third benefiting those making $460,000 or more [3].
- Opportunity Zones: The continuation of "opportunity zones" also primarily benefits wealthy investors [3].
Economic Projections and Contrasting Views
- Low and Middle-Income Earners:
- Potential Losses: In contrast, analyses that account for the spending cuts to social safety net programs show that the lowest earners could lose income. The Penn Wharton Budget Model indicates that Americans making between $17,000 and $51,000 could lose about $700, while those earning less than $17,000 could lose more than $1,000 on average [1]. The Yale Budget Lab projects a 5% reduction in after-tax-and-transfer income for the lowest earners when spending cuts are considered [1]. The CBO estimates that the bottom 10% of households would see their income fall by 2% in 2027 and 4% in 2033 [3].
- Limited Benefits from Tax Cuts: While the bill includes some tax benefits for lower earners, such as the increased child tax credit and exemptions for tips and overtime, their impact may be limited. For example, roughly one-third of tipped workers do not pay federal income tax, meaning they would not benefit from a tax deduction on tips [3].
- Impact of Spending Cuts: The proposed cuts to Medicaid (estimated $700 billion through 2034) and SNAP (estimated $267 billion through 2034) would significantly affect low-income households that rely on these programs [3]. Kent Smetters, faculty director of the Penn Wharton Budget Model, notes that while some low-income individuals not receiving these benefits might be slightly better off, the overall impact on those who rely on them would be negative [3].
- Tariff Impact: Increased prices from tariffs, if implemented, would further exacerbate financial strain on low-income households, as they spend a larger share of their income on goods that would become more expensive [1].
- Debt Impact: Analysts project the bill could add $3 trillion to $5 trillion to the national debt over the next decade [1]. Moody's Ratings cited rising debt when it downgraded the country's credit rating on May 16 [1]. The Penn Wharton Budget Model estimates the bill would increase federal debt by 7.2% [1].
- Economic Growth: The White House Council of Economic Advisers (CEA) argues that the tax cuts would strengthen the economy, driving up incomes and wages, with a typical family seeing a take-home pay increase of $7,800 to $13,300 [1]. The House Ways and Means Committee also claims the bill would boost short-run real GDP by 3.3% to 3.8% and long-run real GDP by 2.6% to 3.2%, securing 6 million jobs [4].
- Nuanced Economic Impact: However, the Penn Wharton Budget Model, while projecting a 0.5% higher GDP under the bill, also suggests that the average wage would fall "slightly" over the next decade [1]. This model indicates that any positive economic gains would be driven by changes to programs like Medicaid and SNAP, which would push more lower-income Americans to increase their working hours and savings, essentially coming at their expense [1] [3].
In summary, while proponents argue the bill will benefit all Americans and boost the economy, independent analyses consistently show that its primary financial advantages accrue to the wealthiest individuals and corporations, often at the expense of the most vulnerable populations through significant cuts to social safety net programs [1] [3].
Authoritative Sources
- How much will Trump's tax bill save you? Gains could vary by income. [USA Today]↩
- What's in Trump's House-passed "one big, beautiful bill". [CBS News]↩
- There's a stark contrast between the effects on high earners and those on low-income households in a sprawling legislative package House Republicans passed Thursday. [CNBC]↩
- The One, Big, Beautiful Bill Delivers on President Trump’s Priorities to Restore and Expand Trump-Era Growth and Relief for Families, Workers, and Small Businesses. [House Ways and Means Committee]↩

Answer Provided by www.iAsk.ai – Ask AI.
Sign up for free to save this answer and access it later
Sign up →